The Problem: Powerful AI That Still “Makes Things Up”
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or Claude can write, code, and explain concepts — but they have one major limitation: their knowledge is frozen in time.
That means if a model was last trained in 2023, it doesn’t know what happened after that — new events, updated data, or company-specific information.
This is why chatbots sometimes give answers that sound confident but are actually wrong — or even hallucinate completely false information.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG, short for Retrieval-Augmented Generation, is a technique that allows a language model to pull in external information before generating a response.
In simple terms, instead of relying only on what it “remembers,” the AI can now look things up in real time.
For example, if you ask a company chatbot:
“How many vacation days do I have left this year?”
Without RAG, the model would have no clue — that data isn’t in its training set.
With RAG, the system will:
- Retrieve relevant information from the company’s HR database.
- Combine that data with your question.
- Feed both into the LLM to produce an accurate, personalized answer.
Result: The chatbot gives a real, context-aware response — not a generic guess.
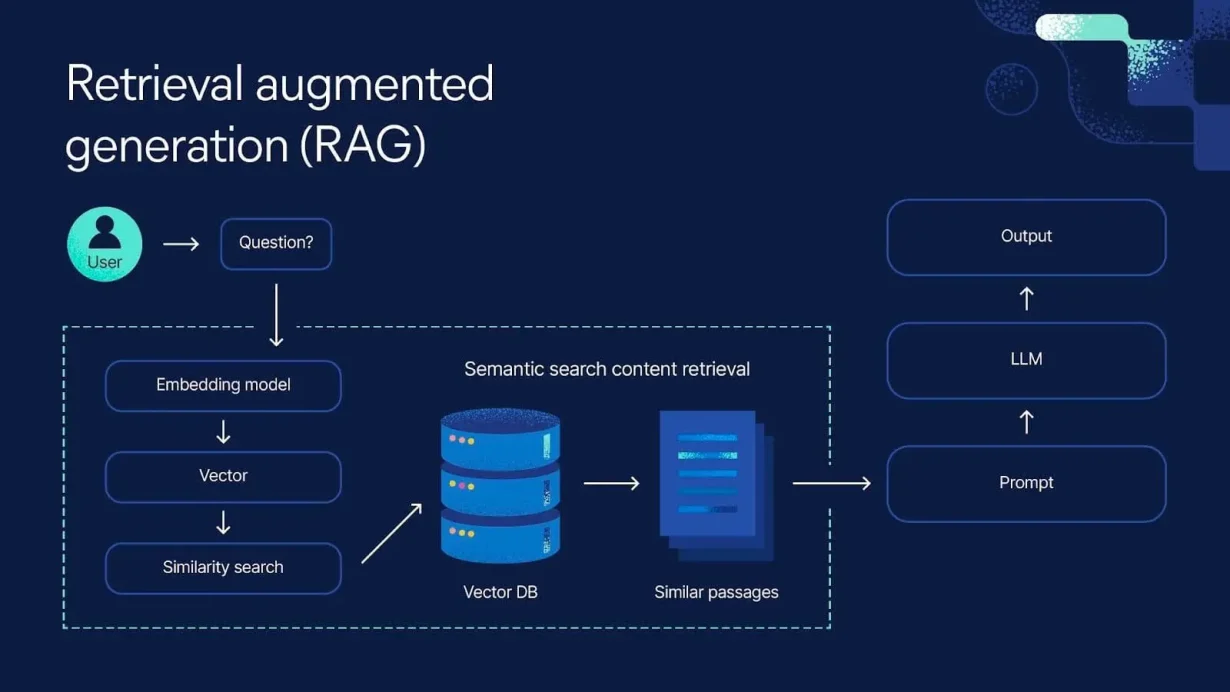
How RAG Works
A typical RAG system has three main stages:
1. Understanding the Query (Prompt Understanding)
The user enters a question in natural language.
The system analyzes it to identify intent — whether it’s asking for data, a summary, or an explanation.
2. Retrieving Relevant Information (Retrieval)
The AI searches through an external knowledge source — such as internal documentation, databases, or indexed web pages — and extracts the most relevant snippets.
3. Generating the Answer (Augmented Generation)
The retrieved text is combined with the original prompt and sent to the language model (like GPT or Claude).
The LLM then generates a complete, context-rich answer based on both its knowledge and the retrieved data.
This means the AI no longer has to “memorize everything” — it just needs to know how to find the right information.
Real-World Use Cases
Many companies are already implementing RAG in their data and support workflows.
- Banks use RAG to help chatbots answer questions based on internal compliance rules.
- Software companies use it for technical assistants that can read and explain documentation.
- Organizations like Uber, Zapier, and OpenAI use RAG to let employees query internal databases using plain language.
With RAG, teams no longer need to retrain their models whenever new information becomes available — they just update the knowledge base.
Benefits of RAG
- Always up to date:
RAG allows AI to access new information without retraining the model. - Personalized for your business:
It lets you connect AI directly to internal documents and data. - Cost-efficient:
No need to re-train huge models — just update the retrieval source. - Reduces hallucinations:
When the model references real, verified data, it’s less likely to produce incorrect or made-up answers.
Limitations of RAG
- Data quality matters:
If the source data is outdated or poorly structured, the model can still generate wrong answers. - Retrieval accuracy:
If the system retrieves irrelevant or misleading information, the output will be off-target. - Initial setup complexity:
You need to design a good retrieval pipeline, search engine, and data organization for RAG to work well.
The Future of RAG: AI That “Looks Things Up”
RAG represents a major step toward AI that doesn’t just recall information — it reasons and references.
It’s becoming the backbone of modern enterprise chatbots, which can understand language and access live, trusted data in real time.
In the future, RAG will likely merge with Agentic AI — systems that can automatically search, synthesize, and act on information — helping humans work faster and more accurately.
RAG vs MCP – What’s the Difference?
As AI systems evolve, a new concept called Model Context Protocol (MCP) is gaining attention — and it’s often compared to RAG.
While both help AI models work with external data, they solve different problems.
| Feature | RAG | MCP |
| Main goal | Improve responses by retrieving relevant text before generation | Provide a standardized way for models to access external tools, APIs, or data sources |
| How it works | Uses a search or retrieval system to fetch information and feed it into the model’s context | Uses a protocol that connects the model to external systems (e.g., databases, APIs, software) via secure adapters |
| Focus area | Knowledge augmentation (improving what the model knows) | Context connectivity (improving what the model can do) |
| Example use | Chatbot finds the right paragraph from internal docs before answering | AI agent queries a live API, pulls structured data, and updates results automatically |
| Integration level | Sits on top of an LLM | Works as a standardized bridge between LLMs and external environments |
In short, RAG helps AI “know more,” while MCP helps AI “do more.”
They can even work together: RAG retrieves information, and MCP enables the model to act on that information — for example, running a query, updating a database, or calling a real API.
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is redefining how AI learns and responds.
Instead of relying solely on memory, AI can now explore, retrieve, and understand new data dynamically.
That means more accurate answers, fewer hallucinations, and smarter tools for businesses.
If you’re planning to build your own AI solution, RAG is the perfect place to start.