Every day, Uber processes billions of records about trips, users, fares, and operations. To analyze this massive amount of data, employees traditionally needed to write complex SQL queries. This process took time and required deep technical knowledge of Uber’s data infrastructure.
To solve this problem, Uber built QueryGPT, an AI tool that translates plain English questions into SQL code.
For example:
“How many trips were completed yesterday in Seattle?”
QueryGPT automatically generates the correct SQL query to fetch the answer in seconds.
How QueryGPT Works
QueryGPT began as a project during an internal Uber hackathon in 2023. It quickly evolved into a key AI product supporting the company’s data operations.
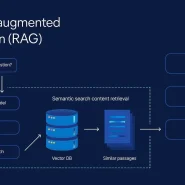
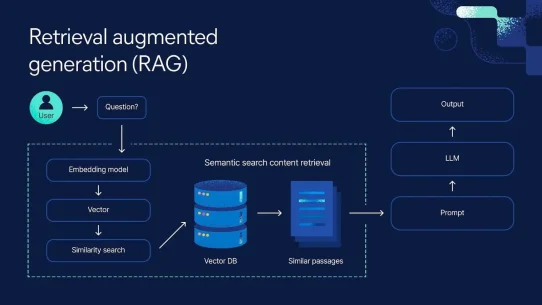
At its core, QueryGPT combines a Large Language Model (LLM) with a method called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Instead of relying solely on the model’s internal knowledge, the system searches Uber’s metadata – such as tables, schemas, and query samples – and then uses the LLM to generate precise SQL statements.
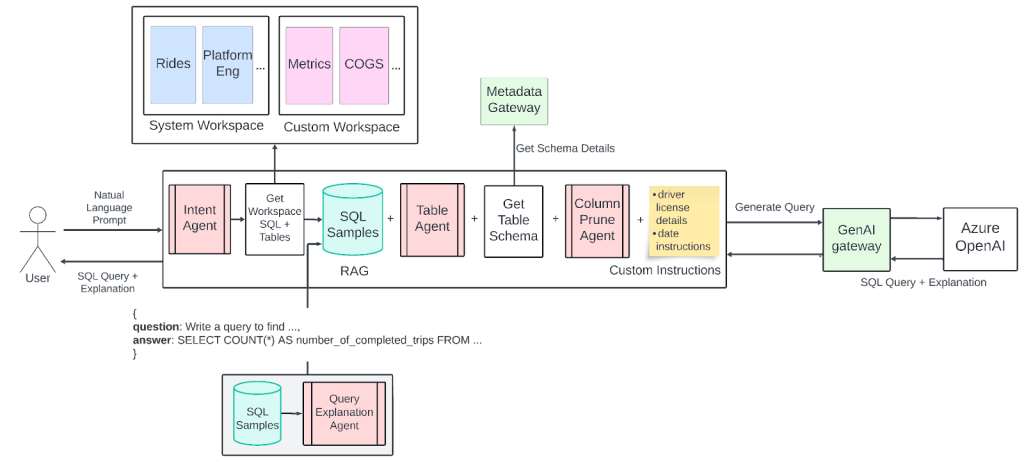
Figure 1: QueryGPT Architecture
Intent Agent
This module analyzes the user’s question to determine intent and selects the right workspace, such as Mobility, Ads, or Delivery.
Table Agent
The Table Agent suggests the most relevant data tables based on the user’s intent. Users can confirm or adjust these tables before running the final query.
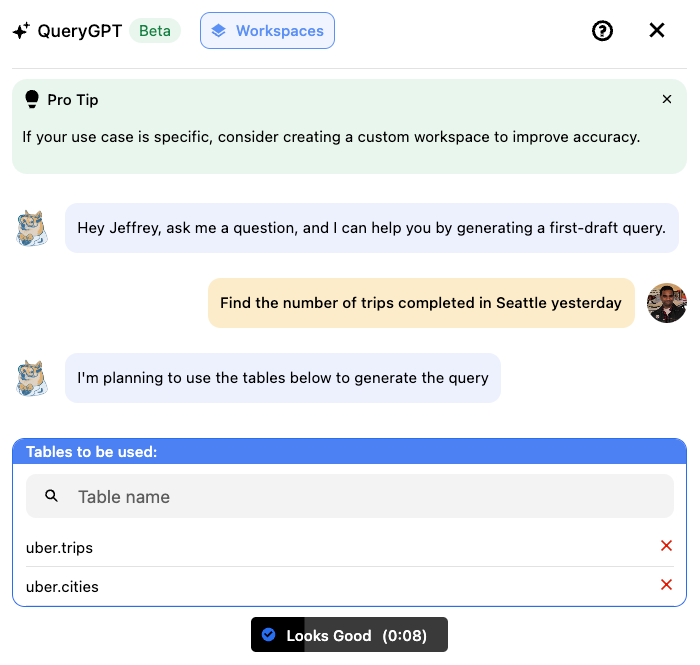
Figure 2: QueryGPT Table Agent
Column Prune Agent
This part of the system removes unnecessary columns from the query. It helps the LLM focus on essential data, saving tokens and improving overall performance.
Thanks to this modular design, QueryGPT understands context and generates accurate, efficient queries for Uber teams.

Figure 3: QueryGPT Prune Agent
Real-World Results
Uber reports that more than 300 employees now use QueryGPT daily. Around 78 percent of users say it saves them significant time when writing SQL queries.
To measure effectiveness, Uber created a “golden dataset” of question–SQL pairs. QueryGPT’s performance is evaluated based on:
- Accuracy of intent understanding
- Table overlap with reference queries
- Whether the generated query runs successfully
- Similarity to the benchmark SQL syntax
Challenges and Lessons Learned
Despite its success, QueryGPT still faces challenges. Like many LLM-based tools, it can sometimes hallucinate, producing non-existent tables or columns. This usually happens when the input question lacks context.
To address this, Uber is developing a prompt enhancer that automatically adds missing context before sending the query to the LLM.
Another key lesson from Uber’s experience is the importance of user-centered design. By defining specific user personas – such as data analysts and operations managers – Uber can tailor QueryGPT’s experience to real workflows and ensure that AI adds genuine value.
Conclusion
QueryGPT demonstrates how AI can lower technical barriers in data analysis. It empowers non-technical employees to access insights and make data-driven decisions without needing deep SQL expertise.
Although challenges like hallucination and context gaps still exist, Uber’s approach shows that AI, when designed thoughtfully, does not replace people. Instead, it enhances their ability to work smarter and faster.
Image credit: Uber Engineering Blog.
Read more: https://www.uber.com/en-VN/blog/query-gpt/